Wave propagation is the process of disturbances that occurs in a regular and organized way. Most commonly, surface waves are formed by the movement of water droplets. While mechanical waves requires a medium to travel, the electromagnetic waves do not require a medium, they can be propagated through vacuum.Propagation depends on the medium's properties.
On the other hand, transverse and longitudinal waves can also be distinguish from each other using the direction of their oscillation. They can also be propagated using vacuum. In physics, waves and vibrations are important phenomena.
They can be considered as disturbances that travel through space-time.
Feedback waves are produced by the movement of a medium, which is usually not associated with mass transport. Instead, they are composed of vibrations. Waves are not mass-producing objects. Instead, they are moving mass perpendicular to the path of propagation. For instance, if a ball is floating in the air, it will not come toward the shore as it travels toward the sea.
There are many types of waves, but they all move. For instance, if a sound waves from an object makes its way to your ear, then the light waves from the Sun will bounce off of it.Although it isn't difficult to prove that waves move, it is often difficult to explain their concept. For instance, waves can carry large amounts of energy. Wave propagation is the scientific term for the movement of waves. In this article, we will discuss the various ways in which waves can move and how they differ from each other.
It has been widely believed that waves require a material to travel through. However, electromagnetic waves, which are usually composed of infrared, ultraviolet, and radio waves, can travel through a material. The fastest moving waves are those that can reach velocities of 3 to 10 meters per second. The speed depends on the material they're traveling through and the temperature of the medium.
The speed at which waves can travel depends on the mass of the medium and the orientation of the particles. Generally, denser materials such as Jello have lower wave velocities. Since waves are moving faster when they're heated than when they're fresh, they tend to have higher wave velocities. Also, stretched out materials such as salt-water taffy have higher wave velocities.
MECHANICAL WAVES
A mechanical wave is a type of oscillation that's responsible for transferring energy through a medium. Its distance from a fixed point is limited by the medium's transmission. For mechanical waves, the displacement is determined by the wavelength. When the factor exceeds 1, it produces harmonic effects, such as when waves break on the beach.
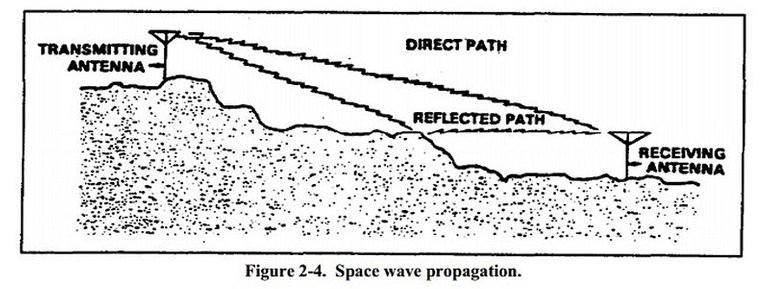
LONGITUDINAL WAVE
A longitudinal wave has a displacement that's parallel to the direction of its propagation. Instead of moving down a tube, the particles do not move as one. Watch a single particle move and observe its motion. The image above shows the difference between the particle's movement and the wave's propagation.
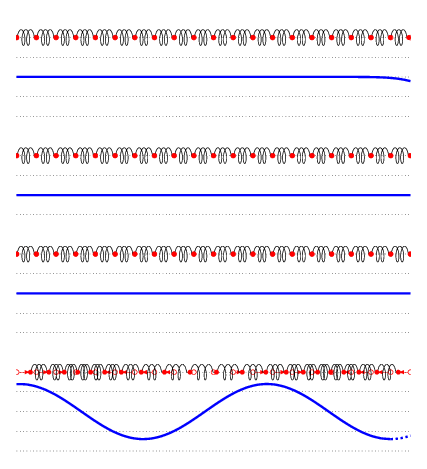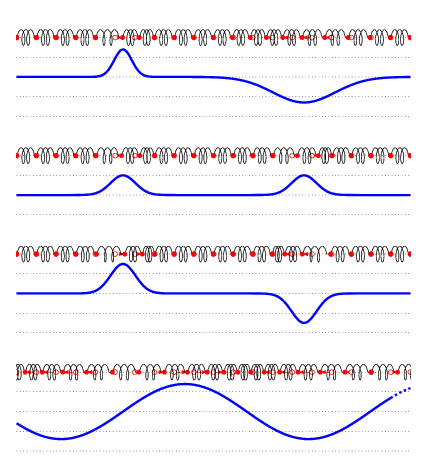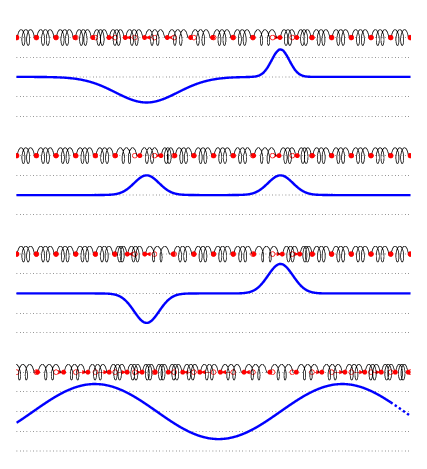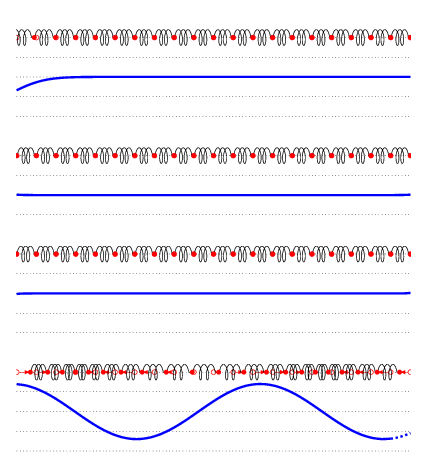
TRANSVERSE WAVE
In a transverse wave, a displacement particle is perpendicular to the path of the wave propagation. As the particle moves along the wave, it does not move with it. Watch the particle's movement. Then, determine if the movement is perpendicular to the energy's motion or if it is at right angles. Transverse waves are known as polarized or electromagnetic waves.

Other types of mechanical waves are listed below, they are combination of both the longitudinal and transverse wave.
WATER WAVE
Water waves are examples of waves that have both transverse and longitudinal motion. When a water wave passes, it moves in clockwise circles. As the water's depth increases, the circles get smaller.
RAYLEIGH SURFACE WAVE
A similar type of wave with longitudinal and transvere motion is known as Rayleigh surface waves can be found in solid bodies. When a surface wave passes through an elliptical path, the resulting wave moves perpendicular to the surface. In an elastic solid, a Rayleigh wave is different from a surface wave.
Since its particles are drawn in clockwise circles, it has a counter-clockwise path. Unlike in water, particles at the surface have a trace of an elliptical path. The Rayleigh surface waves are the most damaging waves during an earthquake. They usually arrive later and have greater amplitudes than S waves.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE
An electromagnetic wave is a type of oscillation that occurs when a magnetic field and an electric current are applied perpendicular to each other. The direction of electromagnetic wave propagation is perpendicular to the force of these fields.
Unlike other waveforms, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium or a field to propagate. They can be polarized and have properties similar to other waves.
There are three methods involved in the ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE which are listed below;
1 Ground Wave is a type of propagation that is commonly used for low-frequency transmissions. It uses the same principle as the waves but uses the ground or Troposphere as its propagation platform.
2 The Sky Wave is a type of electromagnetic wave that uses the ionosphere to propagate. This material is composed of charged ions that are located around 60 to 300 kilometers from the earth's surface. The ionosphere's properties help in the long-distance transmission of electromagnetic waves.
One of the most critical factors that the transmitter must consider is the angle at which the waves are emitted to ensure that they reflect properly on the ground. For long-distance transmissions, such as those using space satellite communication, the use of Space Wave Is is commonly used. This technique involves sending a signal using a straight line from one end of the transmission to the other.
3 For space satellite communication, space waves are used. They send a signal in a straight line and then receive it from the receiver. The height of the tower used for propagation must be high enough to prevent waves from hitting the earth's curvature
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MECHANICAL AND ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
1 Electromagnetic waves diesn need a medium to be propagated whereas the mechanical waves needs a medium for propagation.
2 Examples of mechanical waves includes water, sound and sesimic waves while electromagnetic waves are x-rays, gamma Ray's etec.
3 Electromagnetic waves cab travel through vacuum while mechanical waves can not travel through vacuum.
4 The signals we receive from the light and radio are a typical example of an electromagnetic wave while the mechanical wave example is just like the movement a pool.of water makes after a stone is thrown inside of it.
5 Electromagnetic waves are usually caused or produced by charged particles vibrations whereas the mechanical waves are not usually caused by frequency but are caused by wave amplitudes.
6 A mechanical wave is not just a disturbance like the electromagnetic wave but rather it is known as a periodic disturbance