What Will I Learn?
- Simple Main Concepts
- Data Types (Generally)
Requirements
- RStudio
Difficulty
- Basic
Tutorial Contents
R is a free and open source software which is programming language developed as a statistical computing and graphical environment. RStudio is a powerful and open source integrated development environment for R. In this tutorial, I will explain the R programming Language in a simple way. It will be a long series of tutorials and I will mention all the details you need in R Programming Language.
Simple Main Concepts
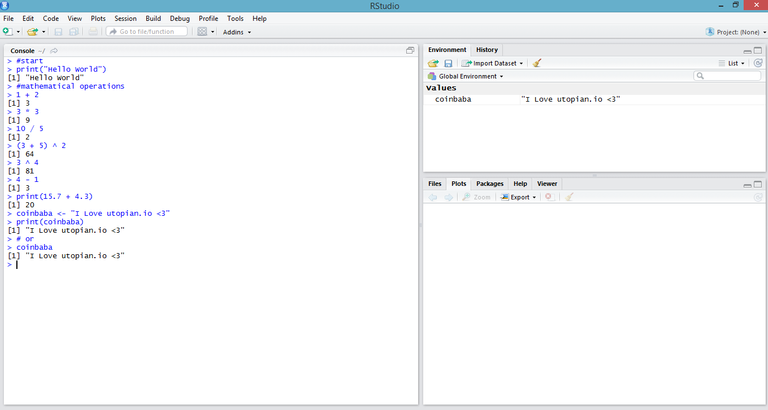
print("Hello World")
[1] "Hello World"
# mathematical operations
1 + 2
[1] 3
3 * 3
[1] 9
10 / 5
[1] 2
(3 + 5) ^ 2
[1] 64
3 ^ 4
[1] 81
4 - 1
[1] 3
print(15.7 + 4.3)
[1] 20
coinbaba <- "I Love utopian.io <3"
print(coinbaba)
[1] "I Love utopian.io <3"
# or
coinbaba
[1] "I Love utopian.io <3"
Here I wrote simple text and mathematical operations. "<-" can be used instead of "=". I will use "<-" throughout the entire tutorial. I created a new value and applied the printing process that I determined with the "print" function. The print ( print() ) function can print any value.
Data Types (Generally)
I'll briefly explain the six data types. In my next tutorial, I will explain the data types in detail. There 6 types of data: Factors, Lists, Data Frames, Arrays, Vectors, and Matrices.| Data Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Numeric | 25, 7, 29, 28.7 |
| Logical | FALSE, TRUE |
| Integer | 2L, 0L |
| Character | "coin", "baba", "coinbaba", "2018" |
| Complex | 1+1i |
| Raw | "coinbaba" is stored as 63 6f 69 6e 62 61 62 61 |
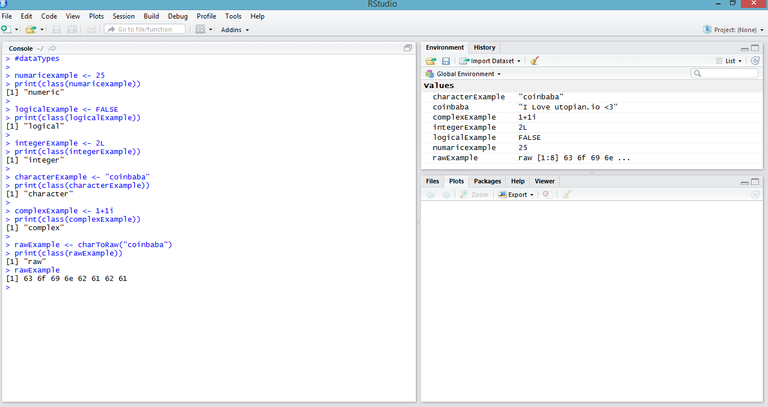
With the print (class (x)) function, we can learn the data type of any value.
numaricexample <- 25
print(class(numaricexample))
[1] "numeric"
logicalExample <- FALSE
print(class(logicalExample))
[1] "logical"
integerExample <- 2L
print(class(integerExample))
[1] "integer"
characterExample <- "coinbaba"
print(class(characterExample))
[1] "character"
complexExample <- 1+1i
print(class(complexExample))
[1] "complex"
rawExample <- charToRaw("coinbaba")
print(class(rawExample))
[1] "raw"
rawExample
[1] 63 6f 69 6e 62 61 62 61
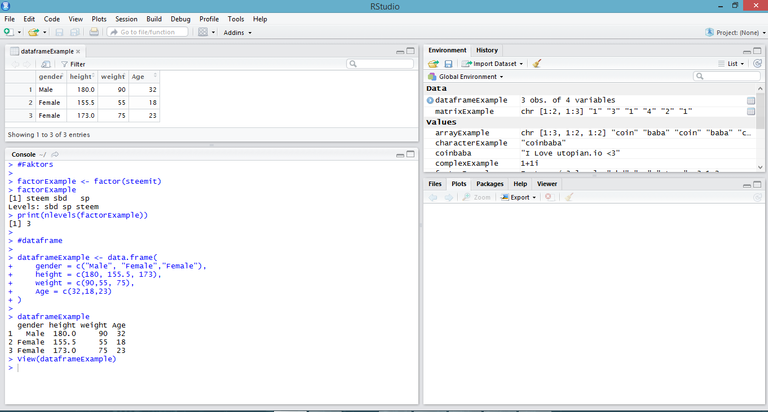
Factors
Factors are r objects created using a vector. Factors are constructed using the factor () function, and the Nlevels functions give the number of levels.
#factors
factorExample <- factor(steemit)
factorExample
[1] steem sbd sp
Levels: sbd sp steem
print(nlevels(factorExample))
[1] 3
Lists
A list is an R object that can contain many different types of elements, such as function, vectors and even other lists.#Lists
listExample <- list(c(1,7,5),10)
listExample
[[1]]
[1] 1 7 5
[[2]]
[1] 10
Data Frames
Data frames are data objects. Unlike a matrix in the data frame, each column can contain different data modes. Data Frames are created using the data.frame () function.
#dataframe
dataframeExample <- data.frame(
+ gender = c("Male", "Female","Female"),
+ height = c(180, 155.5, 173),
+ weight = c(90,55, 75),
+ Age = c(32,18,23)
+ )
dataframeExample
gender height weight Age
1 Male 180.0 90 32
2 Female 155.5 55 18
3 Female 173.0 75 23
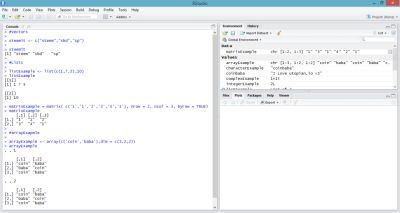
Arrays
Matrices may be limited to two dimensions, and arrays may be of any dimensions. The array function receives a dim attribute that creates the required number of dimensions.
#arrayExample
arrayExample <- array(c('coin','baba'),dim = c(3,2,2))
arrayExample
, , 1
[,1] [,2]
[1,] "coin" "baba"
[2,] "baba" "coin"
[3,] "coin" "baba"
, , 2
[,1] [,2]
[1,] "coin" "baba"
[2,] "baba" "coin"
[3,] "coin" "baba"
Vectors
If you want to create a vector with more than one item, you must use the c() function to combine elements into one value.
#Vectors
steemit <- c("steem","sbd","sp")
steemit
[1] "steem" "sbd" "sp"
Matrices
A matrix is a two-dimensional rectangular data set. The matrix function can be created using a vector entry.
#matrix
matrixExample = matrix( c('1','1','2','3','4','1'), nrow = 2, ncol = 3, byrow = TRUE)
matrixExample
[,1] [,2] [,3]
[1,] "1" "1" "2"
[2,] "3" "4" "1"
Posted on Utopian.io - Rewarding Open Source Contributors
Your contribution cannot be approved because it does not follow the Utopian Rules.
Hi, there are a few problems with your tutorial
For future tutorials I recommend you find an open-source project and make that the subject of your tutorials (for example here).
You can contact us on Discord.
[utopian-moderator]
Thank you for your feedback. I wanted to add simple information because it would be from the beginning, but it was not appropriate for the rules.