
BRIEF INTRODUCTION: Good day everyone all over the world, and I extend my greetings to all my dear readers. I welcome you all once again to this Wonderful CRYPTOCURRENCY NETWORK BLOG, as usual ! all of you know’s, I always carry you along with any information about good crypto related projects through my blog.
According to the main purpose or fixed design of this article , I will be presenting you a brief introduction about blockchain
A blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data (generally represented as a merkle tree root hash)
By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. It is “an open, distributed ledger that can record transactions between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way For use as a distributed ledger, a blockchain is typically managed by a peer-to-peer network collectively adhering to a protocol for inter-node communication and validating new blocks. Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered retroactively without alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus of the network majority. Although blockchain records are not unalterable, blockchains may be considered secure by design and exemplify a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance. Decentralized consensus has therefore been claimed with a blockchain.
Blockchain was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 to serve as the public transaction ledger of the cryptocurrency bitcoin. The invention of the blockchain for bitcoin made it the first digital currency to solve the double-spending problem without the need of a trusted authority or central server. The bitcoin design has inspired other applications, and blockchains which are readable by the public are widely used by cryptocurrencies. Private blockchains have been proposed for business use. Sources such as the Computerworld called the marketing of such blockchains without a proper security model.
The first work on a cryptographically secured chain of blocks was described in 1991 by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta. They wanted to implement a system where document timestamps could not be tampered with. In 1992, Bayer, Haber and Stornetta incorporated Merkle trees to the design, which improved its efficiency by allowing several document certificates to be collected into one block.
The first blockchain was conceptualized by a person (or group of people) known as Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008. Nakamoto improved the design in an important way using a Hashcash-like method to add blocks to the chain without requiring them to be signed by a trusted party.[6] The design was implemented the following year by Nakamoto as a core component of the cryptocurrency bitcoin, where it serves as the public ledger for all transactions on the network.
In August 2014, the bitcoin blockchain file size, containing records of all transactions that have occurred on the network, reached 20 GB (gigabytes). In January 2015, the size had grown to almost 30 GB, and from January 2016 to January 2017, the bitcoin blockchain grew from 50 GB to 100 GB in size.
The words block and chain were used separately in Satoshi Nakamoto’s original paper, but were eventually popularized as a single word, blockchain, by 2016. The term blockchain 2.0 refers to new applications of the distributed blockchain database, first emerging in 2014. The Economist described one implementation of this second-generation programmable blockchain as coming with “a programming language that allows users to write more sophisticated smart contracts, thus creating invoices that pay themselves when a shipment arrives or share certificates which automatically send their owners dividends if profits reach a certain level.
As of 2016, blockchain 2.0 implementations continue to require an off-chain oracle to access any “external data or events based on time or market conditions that need to interact with the blockchain.
IBM opened a blockchain innovation research center in Singapore in July 2016. A working group for the World Economic Forum met in November 2016 to discuss the development of governance models related to blockchain.
According to Accenture, an application of the diffusion of innovations theory suggests that blockchains attained a 13.5% adoption rate within financial services in 2016, therefore reaching the early adopters phase. Industry trade groups joined to create the Global Blockchain Forum in 2016, an initiative of the Chamber of Digital Commerce.
In May 2018, Gartner found that only 1% of CIOs indicated any kind of blockchain adoption within their organisations, and only 8% of CIOs were in the short-term ‘planning or [looking at] active experimentation with blockchain.
In reference with the motion of this article, Today! I will be presenting you a particular undisputed project called: GRABITY
WHAT IS GRABITY?

Grabity: is a public Blockchain project, to transform the Internet paradigm from a centralized network to a distributed network. Current hardware performance has increased dramatically, even enough for smartphones to have better performance than the previous server. However, it does not use 100% storage space or computing power. Anyone can share computer resources through mastered devices such as smartphones, tablets and PCs, and users can receive as many awards as they provide resources, and DApp developers can use shared computer resources to operate services at lower costs. When the Grabity project reaches the commercialization stage, anyone will be able to use distributed nodes to change the Internet paradigm.
The DApps store database is currently on the Blockchain and files are stored on the central server. Because of the limitations of Blockchain’s technology and communication technology, it operates in a hybrid structure. This structure can be used through the Blockchain to some extent but is still vulnerable, but when the server becomes mature, the system will collapse. A truly distributed application must allow files to be used in distribution. However, efficient storage and system systems are needed in managing files on the Blockchain because their capacity increases exponentially.
Because the current Blockchain structure is growing over time, the size of distributed storage that accumulates at each node increases, Network can be reduced by scalability of nodes. However, so that many nodes are free to commercialize the Blockchain. Genesis Hoisting is available for this purpose. Genesis Hoisting is a technology used to connect nodes into the spaces of each node reaching a certain number. The term Genesis Lifts for the process of overwriting files after calculation gives a higher index number than the one in the process of overwriting files after calculation.
The Orbits Network is Grabity's decentralized main net that draw a truly distributed P2P network by utilizing all wired/wirelessly connected idle computer resources. Transactions from Orbits Network are managed efficiently through using Genesis Hoisting technology, which can process transactions simultaneously and quickly. In addition, Smart Contract and resource files can be stored in separate portions into each by using the distributed storage technology and Defrag Function technology that can recall each part and execute in a streaming format.
Anyone can share computer resources through already-possessed idle devices such as smartphones, tablets or PCS, and will be able to contribute in building public Blockchain and transform the Internet paradigm from a centralized system to a distributed network.
GRABITY ECOSYSTEM

.jpg)

The Grabity Ecosystem consists of nodes, communities, DApp, and platforms, and each institution contributes to the ecosystem based on economic tokens. We present the token economy and various requirements for the ecosystem to function and develop as follows.
Network layer: P2P-based overlay network. Verify and then spread transactions between nodes through layers. The principle is to use the most basic network bandwidth.
Data layer: Blockchain data structure and physical storage space. Including Merkle Tree, Hash Function, Data Block, digital sign and others that store blocks and DApp files that contain transaction history.
Agreement Layer: Nodes that generate transactions directly verify transactions themselves, and transactions that have been verified by most of the closest nodes are generated as blocks. This is distributed to other nodes, and if a node is set to be a malicious attack, transaction details are initialized and synchronized with verified transaction details.
Application Layer: Provide an application interface on the Blockchain. Smart contracts, virtual machines, DApp, etc. Included and connected directly between data users.
Layer of Management: Toolkit and SDK are provided to form ecosystem development and place 3rd Parties.
GRABITY PROJECT ROADMAP
2018 Q4 Smart contract Deploy
ERC20 based Token issue
GBT Pre-Sale
2019 Q1 Network Layer Development
(P2P-based overlay network)
Planet Wallet Launching
GBT Public-Sale
2019 Q2 Data Layer Development
Consensus Layer Development
2019 Q3 Testnet Launching
Toolkit & SDK Development
Block Explorer Development
2019 Q4 Application Layer Development
2020 Q1 Management Layer Development
2020 Q2 Orbits Network Launching
GBT-based DEX, DApp Store Launching
GRABITY TEAM BOARD
_edit.png)
GRABITY ICO AND TOKEN REVIEW
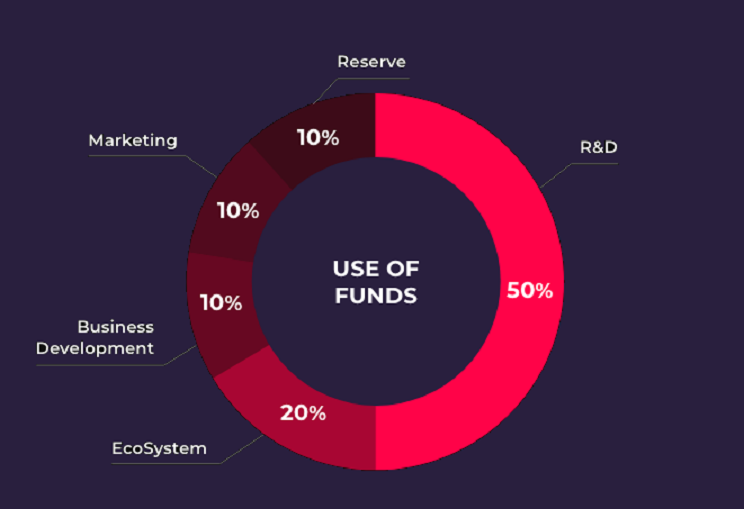
The initial 10,000,000,000 GBT for the development and operation of the project are issued from the Ethereum network. The ERC20-based GBT will be replaced with the Orbits Network-based GBT after the main net launch. In addition, since the main net, GBTs are issued in addition to consideration of the inflation rate for the purpose of compensating computer resource providers. The rate of inflation can be flexible, but will be determined in a way that does not exceed 5% to protect token holders and ecosystem participate.
Tokens except for the pre-sale and public sale are sold in private rounds.
Unsold tokens are due to be incinerated.
Pre Sale
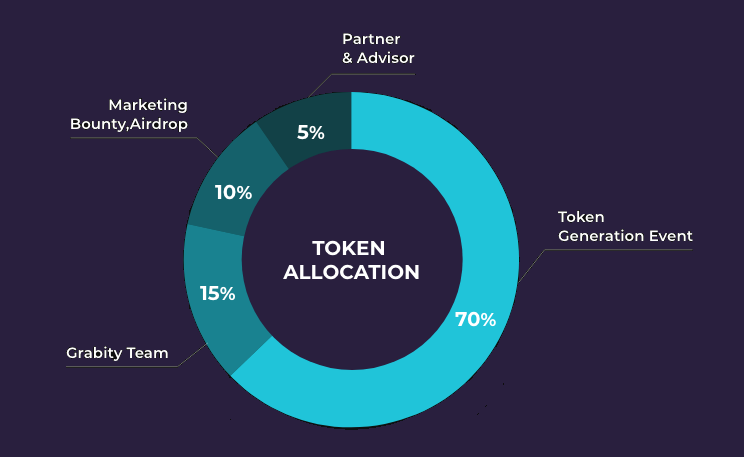
Percentage of sales Token from total Token: 70%
Total Token amount: 10,000,000,000 GBT
Token Token sale amount: 7,000,000,000 GBT
Hard cap : 30,000,000 USD
Soft cap : 10,000,000 USD
The consumers of computer resources can use the Orbits Network using GBT for less than the cost of building or maintaining existing servers, and the provider of computer resources can obtain GBT by providing Orbits Network with idle resources or extra devices of their own devices.
Demand for GBT
Consumers who need computer resources should purchase GBT.
Need to purchase GBT to participate the in the ICO on the Orbits Network-based DApp
GBT is DApp's main currency, and if DApp's users increase, demand can increase.
The reward for providing computer resources after the main net launch can be expected to increase the demand for GBT, determined from the additional computer resources and GBT.
MY OPINION CONCERNING THIS PROJECT
In my own perspective, I can see GRABITY as an innovative, incomparable and undisputed project with a great vision and unique ambition to be the most smartest and respective projects in the nearest future all over the globe.
CONCLUSION:
Nowadays a lot of projects are being created in different countries, But not much of them with solid standard and good qualities as GRABITY does.
For more or further details, please! Kindly follow the links below:
WEBSITE: https://grabity.io
WHITEPAPER: https://github.com/grabityorg
TOKEN SALE: https://grabity.io/sale
TWITTER: https://twitter.com/GrabityOfficial
MEDIUM: https://medium.com/grabityio
FACEBOOK: https://www.facebook.com/Grabity.io
YOUTUBE: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCLNbf55ckVw37CC3CnuEYbw?view_as=subscriber
REDDIT: https://www.reddit.com/user/GrabityOfficial
TELEGRAM: https://t.me/GrabityENG
STEEM: https://steemit.com/@grabity
Great thanks to all my dear readers, you will be more appreciated if you can kindly send a recommendation to some friends and to all media across the globe. Thanks! for given your time.
AUTHOR: Dprince2281